The NRPE addon is designed to allow you to execute Nagios plugins on remote Linux/Unix machines. The main reason for doing this is to allow Nagios to monitor "local" resources (like CPU load, memory usage, etc.) on remote machines. Since these public resources are not usually exposed to external machines, an agent like NRPE must be installed on the remote Linux/Unix machines.
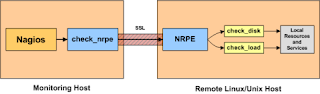
The NRPE addon consists of two pieces:
The check_nrpe plugin, which resides on the local monitoring machine
The NRPE daemon, which runs on the remote Linux/Unix machine
INSTALLATION:
Remote Host Setup:
Create a new nagios user account and give it a password.
/usr/sbin/useradd nagios
passwd nagios
Download nrpe and nagios-plugin.
wget http://osdn.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/nagiosplug/nagios-plugins-1.4.11.tar.gz
tar xvzf nagios-plugins-1.4.11.tar.gz
cd nagios-plugins-1.4.11/
Compile and install the plugins.
./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nagios
make
make install
The permissions on the plugin directory and the plugins will need to be fixed at this point, so run the following commands.
chown nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios
chown -R nagios.nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec
Install the NRPE daemonDownload the source code tarball of the NRPE addon (visit http://www.nagios.org/download/ for links to the latest versions) and execute:
mkdir ~/downloads
cd ~/downloads/
wget http://osdn.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/nagios/nrpe-2.12.tar.gz
tar xzf nrpe-2.12.tar.gz
cd nrpe-2.12/
Compile the NRPE addon.
./configure
make all
Install the NRPE plugin (for testing), daemon, and sample daemon config file.
make install-plugin
make install-daemon
make install-daemon-config
Add the following entry for the NRPE daemon to the/etc/services file.
nrpe 5666/tcp# NRPE
Next we have to add init script for nrpe.For this,
cd nrp-2.12/
cp ./src/nrpe /usr/sbin/
cp ./sample-config/nrpe.cfg /etc /
cat init-script.in > /etc/init.d/nrpe
mod a+x /etc/init.d/nrpe
open the /etc/init.d/nrpe file and edit lines:
NrpeBin=/usr/sbin/nrpe
NrpeCfg=/etc/nrpe.cfg
Then restart nrpe services
/etc/init.d/nrpe restart
Next you have to edit the nrpe configuration file and allow the monitoring of host ipaddress with:
vi /etc/nrpe.cfg
allowed_hosts=127.0.0.1,ipaddress of monitoring host
Then open nrpe port in the remote server firewall. Here I am using apf firewall.
vim /etc/apf/conf.apf
edit the follwing section and add port number 5666
IG_tcp_cports="5666,20...........etc"
restart the services
/etc/init.d/apf restart
Make sure the nrpe daemon is running under xinetd.
netstat -at | grep nrpe
The output of this command should show something like this:
tcp 0 0 *:nrpe *:* LISTEN
Monitoring Host SetupWe have to install nrpe plugin to the monitoring host.
cd ~/downloads
wget http://osdn.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/nagios/nrpe-2.12.tar.gz
tar xzf nrpe-2.12.tar.gz
cd nrpe-2.12/
Compile the NRPE addon.
./configure
make all
Install the NRPE plugin.
make install-plugin
Create a command definition
You'll need to create a command definition in one of your Nagios object configuration files in order to use the check_nrpe plugin. Open the sample commands.cfg file for editing...
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/commands.cfg
and add the following definition to the file:
define command{
command_name check_nrpe
command_line $USER1$/check_nrpe -H $HOSTADDRESS$ -c $ARG1$
}
Now you can add services to your system for monitoring them in the remote system.
You can insert each remote system services in one file.For that you have to edit the configuration file
vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
and append the following line.
cfg_file=/usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/remotehost.cfg
Before adding services, create a new template for each different type of host you'll be monitoring. Let's create a new template for linux boxes.
vi /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/templates.cfg
add the following lines.
define host{
name linux-box ; Name of this template
use generic-host ; Inherit default values
check_period 24x7
check_interval 5
retry_interval 1
max_check_attempts 10
check_command check-host-alive
notification_period 24x7
notification_interval 30
notification_options d,r
contact_groups admins
register 0 ; DONT REGISTER THIS - ITS A TEMPLATE
}
Next you have to edit /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/remotehost.cfg and add the following definitions and services
Define a new host for the remote Linux/Unix box that references the newly created linux-box host template.
define host{
use linux-box ; Inherit default values from a template
host_name remotehost ; The name we're giving to this server
alias Fedora Core 6 ; A longer name for the server
address 192.168.0.1 ; IP address of the server
}
Then, define a new contact for the remote Linux/Unix box that references the generic-contact template.
define contact{
contact_name remote
use generic-contact
alias Nagios client
email remotehost@gmail.com
}
The following service will monitor the CPU load of the remote host. The "check_load" argument that is passed to the check_nrpe command definition tells the NRPE daemon to run the "check_load" command as defined in the
nrpe.cfg file.
define service{
use generic-service
host_name remotehost
service_description CPU Load
check_command check_nrpe!check_load
}
The following service will monitor the the number of currently logged in users on the remote host.
define service{
use generic-service
host_name remotehost
service_description Current Users
check_command check_nrpe!check_users
}
The following service will monitor the free drive space on /dev/hda1 on the remote host.
define service{
use generic-service
host_name remotehost
service_description /dev/hda1 Free Space
check_command check_nrpe!check_hda1
}
The following service will monitor the total number of processes on the remote host.
define service{
use generic-service
host_name remotehost
service_description Total Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_total_procs
}
The following service will monitor the number of zombie processes on the remote host.
define service{
use generic-service
host_name remotehost
service_description Zombie Processes
check_command check_nrpe!check_zombie_procs
}
Remote Host ConfigurationYou have to insert the following command definitions in /etc/nrpe.conf
command[check_users]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_users -w 5 -c 10
command[check_load]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_load -w 15,10,5 -c 30,25,20
command[check_hda1]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_disk -w 20% -c 10% -p /dev/hda1
command[check_zombie_procs]=/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_procs -w 5 -c 10 -s Z
Then restart the nrpe daemon
/etc/init.d/nrpe restart




